Systems Engineering with SysML: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
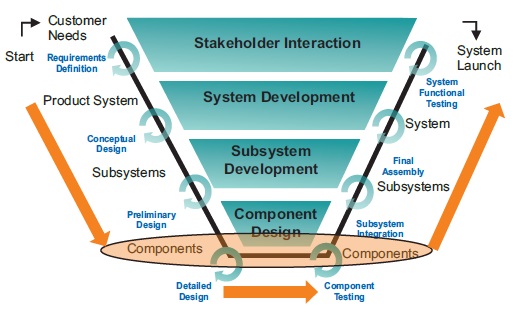
Systems Engineering (SE) is a multidisciplinary approach to the design, development, and lifecycle management of complex systems. Systems Modeling Language (SysML) is a general-purpose modeling language specifically designed for systems engineering. This white paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of SysML and its application in SE.
Understanding SysML
SysML is a modeling language based on the Unified Modeling Language (UML) and is tailored to the specific needs of systems engineering. It provides a visual language for specifying, analyzing, designing, verifying, and validating complex systems.
Key Features of SysML:
- Block Definition Diagram (BDD): Used to define the physical and conceptual elements of a system.
- Internal Block Diagram (IBD): Shows the internal structure of a block, including its components and their relationships.
- Activity Diagram: Represents the flow of activities and decisions in a system.
- Sequence Diagram: Illustrates the interaction between system components over time.
- State Machine Diagram: Models the behavior of a system component in terms of its states and transitions.
- Use Case Diagram: Captures the functional requirements of a system from the user's perspective.
- Requirements Diagram: Specifies the system's requirements in a structured manner.
Applying SysML in Systems Engineering
SysML can be used throughout the entire systems engineering lifecycle, from requirements analysis to system deployment. Key applications include:
- Requirements Engineering: Capturing, analyzing, and managing system requirements.
- System Design: Designing the system architecture, including hardware, software, and human components.
- System Analysis: Analyzing the system's behavior, performance, and safety.
- System Verification and Validation: Ensuring the system meets its requirements and is fit for its intended purpose.
- System Integration and Testing: Integrating system components and testing the overall system.
Benefits of Using SysML
- Improved Communication: Visual models facilitate communication between stakeholders.
- Early Detection of Issues: Identifying and addressing potential problems early in the development cycle.
- Increased System Quality: Ensuring the system meets its requirements and is reliable.
- Reduced Development Costs: Optimizing the design process and minimizing rework.
- Enhanced Traceability: Tracking the relationships between requirements, design, and implementation.
Tools for SysML
Several tools support SysML modeling, including:
- Cameo Systems Modeler: A comprehensive modeling tool for systems engineering.
- MagicDraw: A versatile modeling tool with strong support for SysML.
- Enterprise Architect: A popular modeling tool that supports SysML.
- Open Source Tools: Tools like Papyrus and Topcased offer free options for SysML modeling.
Conclusion
SysML is a powerful tool for systems engineers to model, analyze, and design complex systems. By adopting SysML, organizations can improve their systems engineering processes and deliver high-quality products.
References
- Friedenthal, S., Moore, A., and Steiner, A. (2014). A Practical Guide to SysML: The Systems Modeling Language. Addison-Wesley Professional.
- OMG Systems Modeling Language (SysML) Specification
Would you like to delve deeper into a specific aspect of SysML or its applications in a particular industry?